Rayven’s platform provides powerful, native support for MySQL-based tables that serve as the foundation for storing, querying, and managing structured data in workflows and dashboards.
Whether you're building real-time logic or configuring dashboards, Rayven tables provide the reliable backend needed for persistent data operations.
Table Types and Structure
Rayven supports two types of tables: Primary and Secondary.
1. Primary Tables
-
Used for persistent, long-term storage.
-
Suitable for raw data, logs, calculated metrics, and historical events.
-
Fully read/write capable, with support for inserts, updates, and upserts.
2. Secondary Tables
-
Used for reference data, configuration values, and cached responses.
-
Typically read-heavy, updated less frequently.
-
Ideal for storing lookups (e.g., unit conversions, device mappings).
💡 Tip: Choose based on usage—primary for high-volume transactional data; secondary for lightweight configs or lookups.
Creating Tables
Tables can be created via the Data Tables interface.
Manual Table Creation
-
Navigate to the Tables section in the Data menu.
-
Click “+ New Table”.
-
Define the table name, schema (fields, types), and description.
-
Save and publish the structure.
Auto-Creation via Templates
-
Rayven provides prebuilt templates to auto-generate commonly used tables (e.g., device logs, alert tracking).
-
Once created, tables can be updated, but cannot be deleted, so design carefully.
Writing to Tables in Workflows
To store data in a table:
-
-
Drag in the Update Table Node.
-
Select the target table.
-
Choose the key field (e.g.,
device_id,uid) for row matching. -
Map workflow variables to table columns.
-
Set behavior:
-
Insert only: New records only
-
Update if exists: Modify existing rows
-
Upsert: Insert or update depending on presence
-
-
Reading from Tables in Workflows
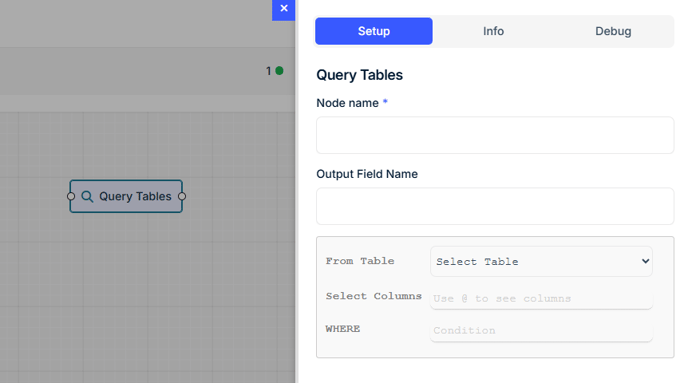
To retrieve data:
-
Use the Query Table Node.
-
Select the table.
-
Apply filter conditions using:
-
Static values (e.g., status = “active”)
-
Dynamic variables from workflow context
-
-
Set result mode:
-
First match
-
Multiple rows
-
All rows (use cautiously)
-
Output data can be:
-
Used in logic nodes
-
Injected into HTML Nodes for dynamic interface display
Table Labels and Filtering
What Are Labels?
Labels are user-defined tags attached to table rows to organize and filter data.
Examples:
-
region = north -
priority = high -
device_type = pump
Applying Labels
-
Manually in the table UI
-
Automatically within a workflow using the Table Update node
Using Labels
| Use Case | Example |
|---|---|
| Query Filtering | Only return rows labeled region=north |
| Workflow Logic | Route based on priority=high |
| Dashboard Filtering | Show only rows matching the user’s site or role |
Query Patterns & Optimization
-
Use indexed fields (IDs, timestamps) for performance.
-
Avoid full-table reads unless necessary—always filter where possible.
-
Use secondary tables for reference data to avoid repeated API calls.
-
Combine label filters and UID variables for granular results.
Best Practices
-
Lock schema in production tables to prevent accidental changes.
-
Use consistent field names (e.g.,
device_id,event_date). -
Regularly archive or purge large primary tables to maintain performance.
-
Document table purposes, schema definitions, and label conventions.
-
Use role-based access control to protect sensitive data.
Q&A
Q: Can I update multiple rows in a table at once?
A: No. Table updates are performed on a per-row basis using a defined key field. To affect multiple rows, loop logic is needed.
Q: What happens if the upsert key field is missing?
A: The row will not update or insert properly. Always ensure that key fields like device_id or uid are populated before the update.
Q: Can I read from multiple tables in the same workflow?
A: Yes. Use separate Query Table Nodes for each table, and merge or compare results using logic or expression nodes.
Q: Can I create relationships between tables?
A: Not directly like SQL JOINs, but you can simulate lookups by querying one table and using the result to filter a second query.
Q: Can I use table data in HTML or dashboards?
A: Absolutely. Query results can be injected into HTML Nodes or used to populate form controls, widgets, or visualizations.
Q: Are table updates real-time?
A: Yes. Table writes occur instantly within the workflow execution context and are available for immediate downstream use.
